This is part 2 of the vCD 9.0 Installation guide.
In the previous section we installed an operating system and database for vCloud Director. In this section we will install the base OS and base software for vCD
NOTE: This section is essentially a copy and paste from the database install section, but with a bit more focus on the vCD aspects
vCD Cell Hardware Reqirements
Configure the vCD Virtual Machine with at least the following specification
This lab will only have one vCD cell:
- OS: CentOS 7
- 20GB Disk
- 6GB Memory
- 2 vCPUs
Full requirements are listed here: https://docs.vmware.com/en/vCloud-Director/9.0/rn/rel_notes_vcloud_director_90.html
vCD can operate with a single IP address however I have encountered issues with single IP vCD installations in the past, so in this example we will configure two interfaces, each with one IP address. (one for HTTP and the other for Console Proxy)
“Each vCloud Director server must support two different SSL endpoints. One endpoint is for the HTTP service. The other is for the console proxy service. These endpoints can be separate IP addresses, or a single IP address with two different ports. You can use IP aliases or multiple network interfaces to create these addresses. You cannot use the Linux ip addr add command to create the second address.”
Install a supported OS.
In this example I’m using CentOS 7 but any of the following are supported:
- CentOS 6
- CentOS 7
- Oracle Linux 6
- Oracle Linux 7
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/vCloud-Director/9.0/rn/rel_notes_vcloud_director_90.html
I like to use a minimal CentOS installation to keep things clean and free from unnecessary bugs and performance issue, you don’t need a UI so CentOS minimal works well for vCD
- Download and boot into the latest CentOS 7 installation media located here http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-1708.iso
Install the operating system with defaults except:
- On the Installation Summary page, select Installation Destination and then Done on the top right
- Also on the Installation Summary page, scroll down to Network and Hostname. Enable each NIC & hit Configure to set the IP addresses. Also set the hostname at the bottom of the screen.
- Ensure that both the Timezone & Keyboard language is correct
- Hit Begin Installation once ready
- Set the root password
- Reboot when prompted
Update the OS and install required components
Connect to the VM with SSH and first update yum:
- yum update yum
Next, update the remainder of the system:
- yum update
- Reboot the guest OS
Install the packages required by vCD. See here for details https://docs.vmware.com/en/vCloud-Director/9.0/rn/rel_notes_vcloud_director_90.html
- yum install alsa-lib bash chkconfig coreutils findutils glibc grep initscripts krb5-libs libgcc libICE libSM libstdc++ libX11 libXau libXdmcp libXext libXi libXt libXtst module-init-tools net-tools pciutils procps redhat-lsb sed tar wget which
Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/vCloud-Director/9.0/rn/rel_notes_vcloud_director_90.html
Install NTP to keep the clock in sync:
- yum install ntp
Configure ntp servers
“You must use a network time service such as NTP to synchronize the clocks of all vCloud Director servers, including the database server. The maximum allowable drift between the clocks of synchronized servers is 2 seconds.”
VMware generally recommends to use at least 4 NTP servers. Using VI, change the lines beginning with server to NTP servers. All components connecting to vCD should share the same NTP servers for accurate timekeeping:
- vi /etc/ntp.conf
Start the ntpd service
- systemctl start ntpd
- systemctl enable ntpd
Ensure ntpd is running:
- systemctl status ntpd
Check ntpd is syncing to correct ntp servers (If you are using a pool, they might not have the same IP/hostname as the pool)
- ntpq -p
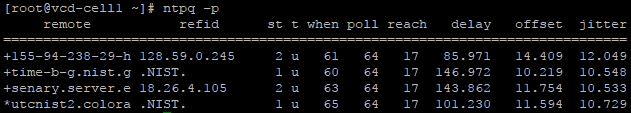
Ensure that the date is set correctly
- date -R
Ensure that the vCD hostname is in DNS as an A record and that you have a PTR set too
“All host names that you specify during installation and configuration must be resolvable by DNS using forward and reverse lookup of the fully qualified domain name or the unqualified hostname”
Verify the above with for example:
- yum install bind-utils (to install nslookup)
- nslookup vcloud
- nslookup vcloud.example.com
- nslookup 192.168.1.1
For this lab environment, I turn off selinux but leave the firewall enabled:
- vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
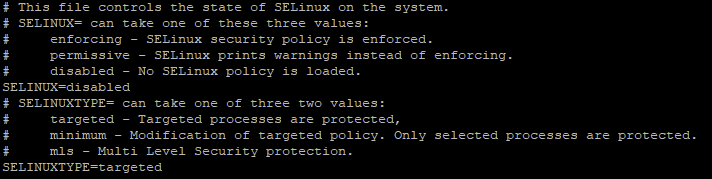
Change SELINUX=enforcing
to
SELINUX=disabled
NOTE: This is line 6 of the config file, not the last line
This change only takes effect on reboot, if you don’t want to reboot now run:
- setenforce 0
Next section: vCloud Director Installation Part 3 – vCloud Director Install








